"HEYDƏR ƏLİYEV İRSİ"
BEYNƏLXALQ ELEKTRON KİTABXANA
"HEYDAR ALIYEV HERITAGE"
INTERNATIONAL ONLINE LIBRARY
- Library is a holy temple for the people and nation, it is the source of knowledge, wisdom and spirituality
H. Aliyev
H. Aliyev
Caucasian Albania
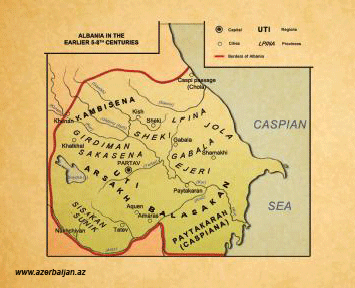 It is considered that Albania as a state existed in IV -III centuries BC. It bordered with the Caucasian Mountains in the north, the Caspian Sea in the east, Iberia in the west, Armenia in the south-west, Atropatene in the south. It means that the territory of the ancient Albania included the present-day Republic of Armenia, a large part of the present Republic of Armenia, southern part of the Republic of Daghestan (Russian Federation), the valley of the Alazani and Iori rivers in Georgia. According to the antique, Albanian and other sources, 26 tribes settled in Albania. The name Albania comes from the Albans, one of the biggest tribes in the Northern Azerbaijan. In the ancient times, Albania stood persistently against the alien invaders and could maintain its independence. According to a tradition referred to by the Albanian historian Movses Kaghankatvatsi, Albania was ruled by King Aran in I century BC. Then the territory of Albania stretched from the River Arax up to Khunakert castle (Kazakh-Borchali region). In 262, the state was incorporated into the Sassanid Empire. In 314, the Albanian ruler Urnair adopted Christianity as an official religion. As a result of the invasions of Arabs, Albania ceased to exist in 705. Its capitals were Kabala (Qabala) and Barda.
It is considered that Albania as a state existed in IV -III centuries BC. It bordered with the Caucasian Mountains in the north, the Caspian Sea in the east, Iberia in the west, Armenia in the south-west, Atropatene in the south. It means that the territory of the ancient Albania included the present-day Republic of Armenia, a large part of the present Republic of Armenia, southern part of the Republic of Daghestan (Russian Federation), the valley of the Alazani and Iori rivers in Georgia. According to the antique, Albanian and other sources, 26 tribes settled in Albania. The name Albania comes from the Albans, one of the biggest tribes in the Northern Azerbaijan. In the ancient times, Albania stood persistently against the alien invaders and could maintain its independence. According to a tradition referred to by the Albanian historian Movses Kaghankatvatsi, Albania was ruled by King Aran in I century BC. Then the territory of Albania stretched from the River Arax up to Khunakert castle (Kazakh-Borchali region). In 262, the state was incorporated into the Sassanid Empire. In 314, the Albanian ruler Urnair adopted Christianity as an official religion. As a result of the invasions of Arabs, Albania ceased to exist in 705. Its capitals were Kabala (Qabala) and Barda.
